Hydrogel for Agriculture
Some semi-synthetic polymers are of great interest for agricultural applications, particularly in arid fields, likewise, because they can be applied to create systems for the slow delivery of nutrients into the soil, which are imperative to increase crop yields utilizing environmentally friendly technologies.
Introduction to Agriculture
Agriculture and food production are crucial sections for sustainable progression. To keep the production procedure of plants efficient, and realize the genetically determined potential of productivity, it is required to optimize the conditions of the environment and anthropogenic factors and to maintain them in the optimal ranges. Hydrogels hold material amounts of both water and nutrients within their three-dimensional polymeric network. In terms of both safety and sustainability, the usage of natural biopolymer-base hydrogels is more profitable.
 Fig. 1 Schematic representation of the slow release of nutrients and
water content from hydrogel during different climate conditions. (Singh, N., et al., 2021)
Fig. 1 Schematic representation of the slow release of nutrients and
water content from hydrogel during different climate conditions. (Singh, N., et al., 2021)
Applications of Hydrogel in Sustainable Agricultural
The network structure of hydrogels is generally formed by physical crosslinking and/or chemical crosslinking between polymer chains. The nature, strength, and extent of crosslinking can be acclimatized to customize gel parcels (such as mechanical strength, porosity, and swelling behavior) to suit a given type of application.
- Plant Cultivation
The growth of plants gets reduced and occasionally eternal damage occurs in soil biota when there is less water retention and filtering of humidity, or high evapotranspiration in soil. Recently, plant bioengineering has provided effective methods to propagate new kinds with advanced yields and better qualities via the use of hydrogel. Hydrogels act as little reservoirs of water and dissolve nutrients that are released in a controlled manner anchored by plant roots via capillary action. Fertilizer and salt release are majorly dependent upon pH and temperature followed by a diffusion-controlled mechanism. Cross-linkers, binders, and fillers play pivotal roles in determining properties, architecture, and hydrogel pores.- Water reservoir
- Controlled micronutrient delivery system
- Stimuli-responsive smart delivery system
- Gene transfection
- Plant growth
- Soil remediation agent
- Nanocarriers for agrochemicals
- Augmented photosynthesis
 Fig. 2 Diagrammatic representation of different applications of hydrogel in agriculture. (Singh,
N., et al., 2021)
Fig. 2 Diagrammatic representation of different applications of hydrogel in agriculture. (Singh,
N., et al., 2021)
- Pest Control
In the field of pest control in agriculture, the most important thing to achieve maximum benefits is slow release, whether it is chemical insecticides or plant essential oils. There are nanocomposite hydrogels that take advantage of both the gelation property of alginate and the adsorption capacity of clays and have great potential in the application of pesticide carriers to improve the utilization efficiency of water-insoluble pesticides.
 Fig. 3 Schematic illustration of (a) (b) the chemical structure and (c)
the key interactions in PMACa hydrogel. (Furui, H., et al., 2019)
Fig. 3 Schematic illustration of (a) (b) the chemical structure and (c)
the key interactions in PMACa hydrogel. (Furui, H., et al., 2019)
- Removal of Harmful Substances
Bacterial pollution is one of the main challenges in the treatment of wastewater. Chitosan beads also gained special attention in the removal of dye, metal ions, bacteria, and organic pollutants due to their excellent properties like high adsorption capacity, ease of modification, and regeneration. To improve its adsorption performance, physical and chemical methods have been applied to modify chitosan to achieve better mechanical strength and higher adsorption capacity and selectivity, as well as other benefits including magnetism and antimicrobial capability.
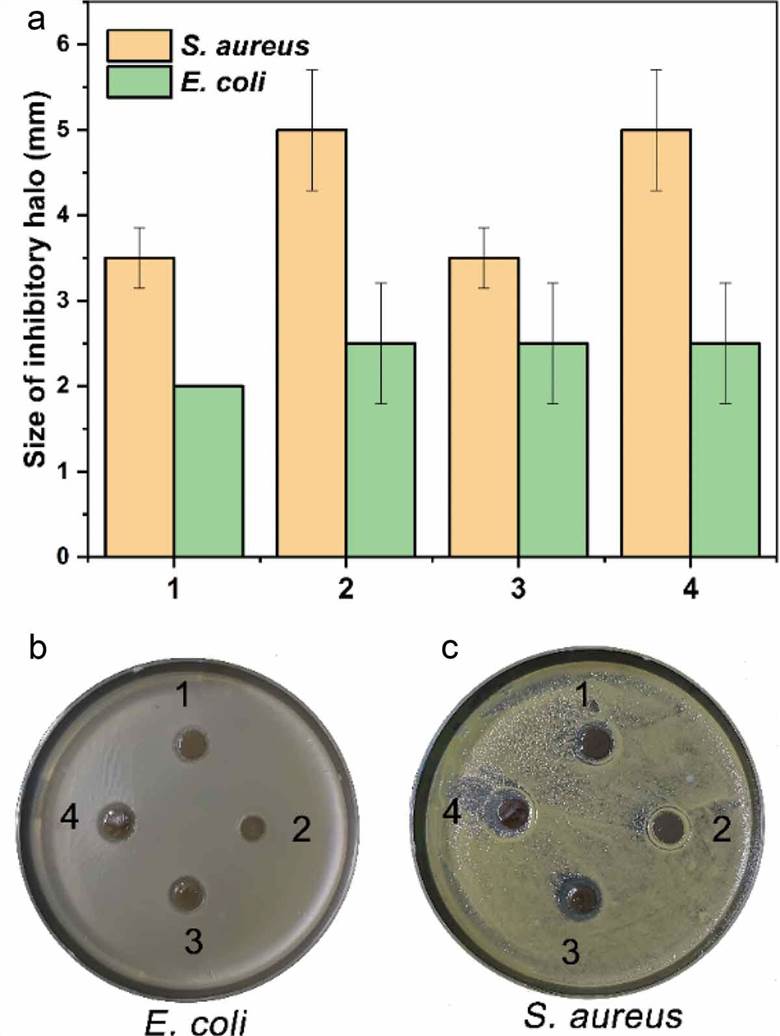 Fig. 4 The
antimicrobial activity of the hydrogels. (Tianwen W., et al., 2020)
Fig. 4 The
antimicrobial activity of the hydrogels. (Tianwen W., et al., 2020)
The Hydrogel Development Services We Provide
In agriculture, hydrogels have their application as soil conditioners and nutrient reservoirs. As a pioneer in field of hydrogel, research and development, Matexcel provides a comprehensive portfolio of hydrogel-related services, including hydrogel development services, and hydrogel analysis and characterization services. Please contact us for more information.
References
- Singh, N.; et al. 3-Dimensional Cross Linked Hydrophilic Polymeric Network "Hydrogels": An Agriculture Boom. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 253, 106939.
- Furui, H.; et al. Fabrication of a sustained release delivery system for pesticides using interpenetrating polyacrylamide/alginate/montmorillonite nanocomposite hydrogels. Applied Clay Science. 2019, 183, 105347. DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2019.105347.
- Tianwen W.; et al. Polyvinyl Alcohol/Sodium Alginate Hydrogels Incorporated with Silver Nanoclusters via Green Tea Extract for Antibacterial Applications, Designed Monomers and Polymers, 2020, 23:1, 118-133, DOI: 10.1080/15685551.2020.1804183.