Hydrogel for Cell Culture
The hydrogel possesses the ability to create a pliable and damp three-dimensional (3D) framework that closely resembles the extracellular matrix (ECM), thereby facilitating cell encapsulation. As a result, these hydrogels have gained significant interest for their potential use as scaffolds in 3D cell cultures.
 Introduction to Cell Culture
Introduction to Cell Culture
Three-dimensional cell cultures offer an efficient in vitro platform for unimpeded cellular proliferation
across all dimensions. In contrast to the two-dimensional culture system, it facilitates a more comprehensive
comprehension of in vivo cell behavior as cells adopt a three-dimensional structure akin to that of living
tissue. The generation of 3D cell cultures involves cultivating cells on scaffolds that mimic the natural
extracellular matrix (ECM) environment.
Utilization of Hydrogel for Cell Culture
The composition of hydrogels can encompass a diverse range of natural, synthetic, and semi-synthetic polymers, thereby conferring distinct biochemical, physical, and mechanical properties to facilitate three-dimensional cell culture.
 Fig. 1 Hydrogel and related method of three-dimensional (3D) cell culture preparation. (Park Y,
et al., 2021)
Fig. 1 Hydrogel and related method of three-dimensional (3D) cell culture preparation. (Park Y,
et al., 2021)
- Natural Hydrogels for Cell Culture
Natural hydrogels consist of substances that occur naturally in the body, such as collagen, alginate, hyaluronic acid, and other factors. These substances are essential for supporting various cellular functions and promoting cell survival, growth, and differentiation. Collagen is particularly abundant in the extracellular matrix (ECM) and is therefore an ideal choice for creating three-dimensional cell culture gels.
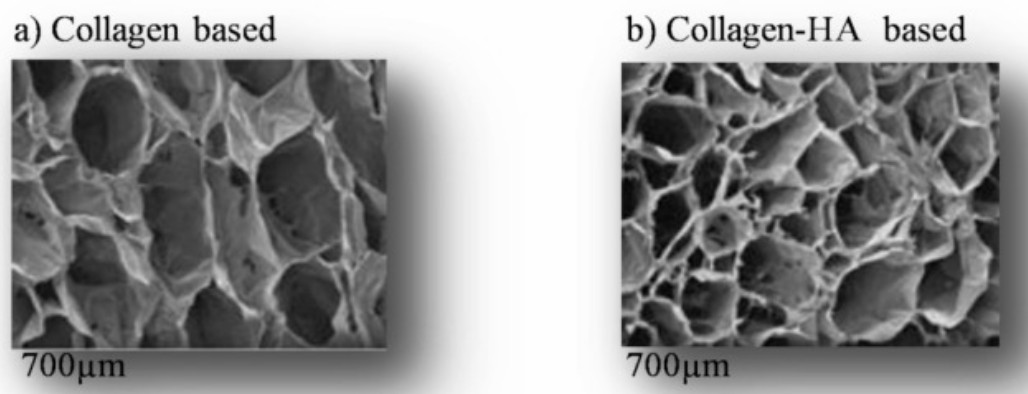 Fig. 2 The schematic of scanning electron microscopy micrographs of freeze-dried
scaffolds collagen based. (Habanjar O, et al., 2021)
Fig. 2 The schematic of scanning electron microscopy micrographs of freeze-dried
scaffolds collagen based. (Habanjar O, et al., 2021)
- Synthetic Hydrogels for Cell Culture
The production of synthetic hydrogels often involves the polymerization of synthetic polymers, which provide a diverse range of biophysical, mechanical, and biological properties when utilized in 3D cell cultures. These synthetic hydrogels possess active chemical groups (such as amine, acid, or alcohol functionalities) that are capable of undergoing chemical reactions. This enables the creation of a well-defined extracellular matrix model with distinctive characteristics.
 Fig. 3 The schematic of polystyrene well insert holder for 3D culture Alvetex Scaffold. (Habanjar O, et al.,
2021)
Fig. 3 The schematic of polystyrene well insert holder for 3D culture Alvetex Scaffold. (Habanjar O, et al.,
2021)
- Semi-synthetic Hydrogels for Cell Culture
Semi-synthetic hydrogels consist of a combination of natural and synthetic polymers, which effectively address the limitations associated with both natural and synthetic hydrogels in 3D cell cultures. In comparison to their natural and synthetic counterparts, semi-synthetic hydrogels possess properties that closely resemble the microenvironment of the extracellular matrix (ECM), exhibit faster relaxation under stress, and create a cellular environment that closely mimics conditions found in living organisms.
The Hydrogel Development Services We Provide
With professional equipment and experienced specialists, Matexcel provides high-quality natural hydrogel development services, synthetic hydrogel development services, fibrin-based hydrogel development services, and poly(vinyl alcohol)-based hydrogel development services. Please contact us for more information.
References
- Park Y.; et al. Applications of Biomaterials in 3D Cell Culture and Contributions of 3D Cell Culture to Drug Development and Basic Biomedical Research. Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 2;22(5):2491.
- Habanjar O.; et al. 3D Cell Culture Systems: Tumor Application, Advantages, and Disadvantages. Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 11;22(22):12200.